REGDOC-2.1.2: Safety Culture
Preface
This regulatory document is part of the CNSC’s Management System series of regulatory documents. The full list of regulatory document series is included at the end of this document and can also be found on the CNSC’s website.
Over the past few decades, experience in the international nuclear industry and other industries has demonstrated the importance of a healthy safety culture in maintaining the safety of workers, the public, and the environment. An organization that actively fosters a healthy safety culture can have a powerful influence on employee attitudes and behaviours, and consequently on individual and corporate safety performance.
Regulatory document REGDOC-2.1.2, Safety Culture, sets out requirements and guidance for fostering a healthy safety culture.
REGDOC-2.1.2 is intended to form part of the licensing basis for a regulated facility or activity within the scope of the document. It is intended for inclusion in licences as either part of the conditions and safety and control measures in a licence, or as part of the safety and control measures to be described in a licence application and the documents needed to support that application.
For proposed new facilities: This document will be used to assess new licence applications for reactor facilities.
Guidance contained in this document exists to inform the applicant, to elaborate further on requirements or to provide direction to licensees and applicants on how to meet requirements. It also provides more information about how CNSC staff evaluate specific problems or data when they review licence applications. Licensees are expected to review and consider guidance; should they choose not to follow it, they should explain how their chosen alternate approach meets regulatory requirements.
For existing facilities: The requirements contained in this document do not apply unless they have been included, in whole or in part, in the licence or licensing basis.
A graded approach, commensurate with risk, may be defined and used when applying the requirements and guidance contained in this regulatory document. The use of a graded approach is not a relaxation of requirements. With a graded approach, the application of requirements is commensurate with the risks and particular characteristics of the facility or activity.
An applicant or licensee may put forward a case to demonstrate that the intent of a requirement is addressed by other means and demonstrated with supportable evidence.
Important note:
Where referenced in a licence either directly or indirectly (such as through licensee-referenced documents), this document is part of the licensing basis for a regulated facility or activity.
The licensing basis sets the boundary conditions for acceptable performance at a regulated facility or activity, and establishes the basis for the CNSC’s compliance program for that regulated facility or activity.
Where this document is part of the licensing basis, the word "shall" is used to express a requirement to be satisfied by the licensee or licence applicant. "Should" is used to express guidance or that which is advised. "May" is used to express an option or that which is advised or permissible within the limits of this regulatory document. "Can" is used to express possibility or capability.
Nothing contained in this document is to be construed as relieving any licensee from any other pertinent requirements. It is the licensee’s responsibility to identify and comply with all applicable regulations and licence conditions.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
A healthy safety culture is a key factor in reducing the likelihood of safety-related events and mitigating their potential impact, and in continually improving safety performance. All workers have a shared responsibility to ensure that a healthy safety culture is a priority.
The CNSC defines safety culture as the characteristics of the work environment, such as the values, rules, and common understandings that influence workers’ perceptions and attitudes about the importance that the licensee places on safety.
The approach taken in this regulatory document is based upon the following principles:
- Every organization has a safety culture.
- Safety culture is influenced by external and internal factors including all workers.
- Safety culture is complex and constantly changing.
- Safety culture needs to be assessed and monitored to achieve the common goal of understanding and limiting risk.
- Safety culture assessment and improvement activities are informed by a defined framework of key characteristics known to reflect a healthy culture.
A healthy safety culture is an interpretation of how safety is integrated into everyday work and interactions, rather than a program to be managed. It is reinforced in how people work together to create a deeper understanding of safety. Monitoring to understand safety culture forms the foundation for building systemic safety improvements over time. Monitoring may include a wide range of methods, from simple workplace observations and interactions to comprehensive assessments of safety culture in larger organizations. A mature and continually improving safety culture manifests itself through everyday safety-related discussions, decisions and actions.
Security culture is a major component of safety culture. Security culture is defined as the assembly of characteristics, attitudes and behaviour of individuals, organizations and institutions that support and enhance nuclear security. [1]
Safety culture and security culture coexist and reinforce one another through the shared common objective of limiting risk, and they share common goals and techniques for promotion and monitoring activities. In this document, "safety culture" denotes safety culture and security culture collectively, except where a distinction is made.
1.1 Purpose
This regulatory document establishes requirements and guidance for fostering and assessing safety culture.
1.2 Scope
The document outlines requirements and guidance in sections 2, 3 and 4. Section 2 also outlines the requirement to articulate a commitment to fostering safety culture, and is intended for licensees of Class I nuclear facilities and uranium mines and mills. Sections 3 and 4 are intended for nuclear power plants and outline the requirements and guidance for safety culture assessments. The requirements and guidance in this document may be used by other licensees applying a graded approach. For more information, see appendix A.
This document provides more specific requirements and guidance related to safety culture, as an elaboration on the management system requirements contained in the CSA standard CSA N286, Management system requirements for nuclear facilities. [2]
1.3 Relevant legislation
The following provisions of the regulations made under the Nuclear Safety and Control Act are relevant to this regulatory document:
- Paragraph 3(1)(e) of the General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations (GNSCR) states that an application for a licence shall contain "the proposed measures to ensure compliance with the Radiation Protection Regulations, the Nuclear Security Regulations and the Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations, 2015;"
- Paragraph 3(1)(k) of the GNSCR states that "An application for a licence shall contain the following information: the applicant’s organizational management structure insofar as it may bear on the applicant’s compliance with the Act and the regulations made under the Act, including the internal allocation of functions, responsibilities and authority;"
- Paragraphs 12(1)(a), (b), (c), (f) and (j) of the GNSCR state that "Every licensee shall
(a) ensure the presence of a sufficient number of qualified workers to carry on the licensed
activity safely and in accordance with the Act, the regulations made under the Act and the licence; (b) train the workers to carry on the licensed activity in accordance with the Act, the regulations made under the Act and the licence;
(c) take all reasonable precautions to protect the environment and the health and safety of persons and to maintain security of nuclear facilities and of nuclear substances; ...
(f) take all reasonable precautions to control the release of radioactive nuclear substances or hazardous substances within the site of the licensed activity and into the environment as a result of the licensed activity;...
(j) instruct the workers on the physical security program at the site of the licensed activity and on their obligations under that program;..." - Paragraphs 17(b), (c) and (e) of the GNSCR state that "Every worker shall...
(b) comply with the measures established by the licensee to protect the environment and the health and safety of persons, maintain security, control the levels and doses of radiation, and control releases of radioactive nuclear substances and hazardous substances into the environment;
(c) promptly inform the licensee or the worker’s supervisor of any situation in which the worker believes there may be…(i) a significant increase in the risk to the environment or the health and safety of persons;...
(e) take all reasonable precautions to ensure the worker’s own safety, the safety of the other persons at the site of the licensed activity, the protection of the environment, the protection of the public and the maintenance of the security of nuclear facilities and of nuclear substances." - Subparagraph 4(a)(i) of the Radiation Protection Regulations states that "Every licensee shall implement a radiation protection program and shall, as part of that program,
(a) keep the amount of exposure to radon progeny and the effective dose and equivalent dose received by and committed to persons as low as is reasonably achievable, social and economic factors being taken into account, through the implementation of- (i) management control over work practices,"
1.4 Relevant national and international standards
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has identified the need for regulators and licensees to address safety culture. The IAEA’s framework that supports safety culture is embedded in several safety requirements, standards documents, and safety guides. Safety culture is reflected throughout IAEA Safety Standards Series No. SF-1, Fundamental Safety Principles. This document includes principles concerning the licensee’s primary responsibility for safety, the integration of safety culture with the management system, and the prevention of accidents through the application of defence in depth (SF-1 principles 1, 3, and 8, respectively). SF-1 also underscores the importance of integrating safety and security. [3]
Key principles and elements used in developing this regulatory document are consistent with SF 1, as well as national and international standards, guides and practices. In particular, this regulatory document complements:
- CSA standard N286-12, Management system requirements for nuclear facilities [2]
- the following IAEA publications:
- GSR Part 1, Government, Legal and Regulatory Framework for Safety [4]
- GS-R-3, The Management System for Facilities and Activities [5]
- GS-G-3.1, Application of the Management System for Facilities and Activities [6]
- GS-G-3.5, The Management System for Nuclear Installations [7]
- NS-G-2.4, The Operating Organization for Nuclear Power Plants [8]
- INSAG-24, The Interface Between Safety and Security at Nuclear Power Plants [9]
- INSAG-15, Key Practical Issues in Strengthening Safety Culture [10]
- Safety Reports Series No.11, Developing Safety Culture In Nuclear Activities [11]
1.4.1 Security culture
In IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 7, Nuclear Security Culture, the IAEA has identified the need for licensees, regulators, and states to establish an effective nuclear security culture. This will provide greater assurance of preventing, detecting, delaying and responding to theft, sabotage, unauthorized access, illegal transfer, or other malicious acts involving radioactive material in use, storage, or transport. [1]
In addition, this regulatory document is based in part on the following publications:
- IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 20, Objective and Essential Elements of a State’s Nuclear Security Regime [12]
- IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 13, Nuclear Security Recommendations on Physical Protection of Nuclear Material and Nuclear Facilities (INFCIRC/225/Revision 5) [13]
- IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 14, Nuclear Security Recommendations on Radioactive Material and Associated Facilities [14]
2. Fostering Safety Culture
Licensees shall document their commitment to fostering safety culture in their governing documentation.
Guidance
All licensees are responsible for fostering a healthy safety culture, by promoting and reinforcing a collective commitment to safety that is responsive to the risk and complexity of the licensed activities. To achieve this, licensees should use all available avenues, including a reliance on governing documentation (i.e., policies, processes, procedures, and manuals) to define and manage safety goals and performance objectives.
The highest level of governing documentation should make safety the utmost priority – overriding the demands of production and project schedules and forming a basis for promoting a healthy safety culture, including a questioning attitude and a commitment to excellence in the performance of all activities important to safety. Governing documentation should describe the leadership role(s) encompassing the highest levels of responsibility for safety matters, as well as areas where workers share safety responsibility. Leaders should use governing documentation to demonstrate key safety behaviours to workers, while ensuring everyone understands their defined safety responsibilities, goals and performance objectives. Promoting and reinforcing a collective commitment to safety includes the continual improvement and practical use of all governing documentation.
The following list is a reference framework for demonstrating a commitment to safety, and describes five characteristics of a healthy safety culture. It includes observable and measurable indicators for each safety culture characteristic and can help licensees clearly demonstrate how they foster safety culture in their organization. The framework is adapted from the IAEA’s GS G 3.1, Application of the Management System for Facilities and Activities [6]; GS-G-3.5, The Management System for Nuclear Installations [7]; and IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 7, Nuclear Security Culture. [1]
Safety culture reference framework
Since healthy safety and security cultures have similar characteristics and indicators, these are consolidated. Indicators that apply only to security culture are marked with an asterisk (*).
- Safety is a clearly recognized value
- Resources are allocated as necessary to ensure safety.
- Multiple mechanisms are used to clearly communicate the value of safety in the organization.
- Timely decisions are made that reflect the value and relative priority placed on safety.
- The importance of safety is documented and demonstrated in the operation of the organization.
- The promotion of a healthy safety culture is prevalent throughout all aspects of the management system.
- Everyone understands that safety, security, and production are closely linked.
- Everyone understands that a credible threat to security exists, and acknowledges that nuclear security is important*.
- There is a sense of urgency to correct significant security weaknesses or vulnerabilities*.
- Accountability for safety is clear
- There are clearly defined roles and responsibilities for all levels and positions in the organization.
- Everyone is held accountable for adherence to established policies and procedures.
- Shared safety responsibilities are delegated to individuals and teams with appropriate authority.
- There is a high degree of compliance with, and understanding of, regulatory requirements.
- Complete and accurate information is provided to the CNSC in a timely and open manner.
- Everyone demonstrates a commitment to safety throughout the organization and an understanding of how they contribute to safety goals.
- Everyone understands how their roles and interfaces contribute to maintaining security*.
- A learning organization is built around safety
- Lessons learned from experiences internal and external to the organization, including successes and challenges, are used as a basis for continual improvement.
- Safety culture assessments, including self-assessments are used to improve performance.
- Processes exist to identify and correct problems in a timely manner, and to develop, implement, and measure the effectiveness of corrective and preventive actions.
- Various training methods are used to maintain and improve professional and technical competence of members of the organization.
- Safety performance indicators are continually developed, tracked, evaluated and acted on.
- Workers are encouraged and recognized for reporting concerns or suspicions, and feel that they have been heard when they voice issues.
- A questioning attitude is maintained by all members of the organization to constantly challenge the safety of day-to-day activities.
- There is systematic development of individual competencies.
- There is an appreciation throughout the organization for diversity of opinion.
- Lessons learned are shared with domestic and international partners.
- Safety is integrated into all activities in the organization
- There are good housekeeping practices, well maintained materials and equipment, and good working conditions in place.
- Documentation and processes, from planning to implementation and review, are complete and followed in accordance with management system requirements.
- Safety performance indicators are continually tracked, trended and evaluated in order to monitor safety; ineffective performance indicators are refined and improved to ensure they continually reflect the health of the licensee’s safety culture.
- A comprehensive approach to safety and security is integrated throughout the organization.
- Workers have the necessary knowledge of work processes and adhere to them.
- Workers are involved in risk assessment and decision-making processes.
- Workers are empowered to address issues related to nuclear security matters*.
- A safety leadership process exists in the organization
- All workers are involved and motivated in promoting a healthy safety culture.
- Managers are visible and actively involved in both preventive and reactive safety-related activities.
- Change management processes are in place and are followed to achieve orderly transitions.
- Collaboration, mutual respect, safety conscious behaviour and teamwork are encouraged, supported and recognized.
- Commitment to safety is evident at all levels of the organization.
- The impact of informal leaders on safety culture is recognized and leveraged to continually improve safety culture.
- There are clear expectations and policies to support open communications.
- Managers communicate clear expectations for performance in areas that affect safety and security.
- A proactive and long-term approach to safety is demonstrated in decision making.
- Managers recognize and take charge of all security weakness or vulnerabilities*
- Managers do not abuse authority to circumvent security*.
- Managers seek continual improvement in security and work to prevent complacency from compromising overall security objectives*.
3. Safety Culture Assessments
Licensees shall conduct comprehensive safety culture assessments that are empirical, valid, practical and functional. Safety culture assessments shall be conducted at least every three years.
Guidance
The purpose of monitoring safety culture is to understand how safety manifests itself in everyday discussions, decisions and actions. A safety culture assessment allows an organization to understand its practical treatment of safety, and to identify areas and actions for improvement. Organizations engaged in complex work involving many interdependent workers and processes will benefit from comprehensive monitoring, which can include safety culture assessments. These assessments use a systematic framework to plan and execute the assessment, respond to findings, and evaluate progress for continual improvement of safety.
A safety culture assessment provides an opportunity for organizational leaders to actively promote and foster a healthy safety culture. Their support for engaging workers in open discussions, decisions and actions on safety ensures an environment of continual safety improvement.
3.1 Objectives applicable to safety culture assessment methods
Adhering to a set of objectives and criteria ensures that safety culture assessments and subsequent findings are reliable and consistent over time. The following four objectives and criteria apply to safety culture assessment methods. Although these are intended for assessments conducted in large organizations, any size or type of licensee may use them to develop, improve and refine safety culture assessment methods.
- Empirical
- What is to be assessed is clearly described.
- Information collected and subsequent analysis is defensible and replicable.
- The method uses structured and objective observations to the extent possible.
- Measures cover the range of cultural characteristics/traits being assessed.
- The method uses a combination of quantitative and qualitative tools in order to build a comprehensive understanding of the licensee’s safety culture.
- Valid
- The method controls for bias and unwanted subjectivity throughout the stages of scope setting, training, data collection, analysis, review and reporting.
- Simultaneous measures of the same construct are validated against one another.
- Practical
- Information obtained from the assessment method is clearly recorded to allow logical analysis.
- The method can be used to assess the entire organization, including a range of different job positions, departments, demographics and lines of work.
- Functional
- The assessment produces a clear interpretation of the organization’s safety culture, based on observable facts.
- The assessment yields relevant, actionable information.
- The method allows for comparative analysis over time.
3.2 Communications strategy
Licensees should develop and implement a communications strategy for the assessment, and consider proactively engaging workers and leaders throughout the assessment process. Where possible, safety culture assessments should be integrated with licensees’ overall communications strategies to ensure timely and consistent messaging. Licensees should consider the timing and frequency of communications, potential communication vehicles, and how to tailor messaging to specific audiences.
Communication with internal stakeholders should take place throughout the safety culture assessment, and the resulting planning and implementation of improvement initiatives. Communication with external stakeholders would typically occur after the assessment is completed.
For security culture, the communications plan must consider that some information is security sensitive; however, for the benefit of greater awareness, all aspects should be shared broadly even if this requires some incidents or lessons learned to be generalized.
A communications strategy should, at the various stages of an assessment and follow-up activities, include a summary of the assessment method, findings and improvement plans. The information should be shared with the following internal and external stakeholders:
- workers
- management
- organizational groups with special functions or requirements (e.g., security, health and safety committees, union representatives, contractors, etc.)
- community groups and the public
- other relevant organizations or individuals
Licensees should expect and encourage feedback from workers and external stakeholders. Feedback from workers can provide insight into the culture of the organization, and feedback from external stakeholders can be used to refine the communications strategy.
3.3 Preparing for the safety culture assessment
3.3.1 Assessment framework
A safety culture framework provides a basis for the systematic review of safety culture against a defined set of characteristics. It also provides a common vocabulary to facilitate communications, and aids in developing improvement plans to address the shared perceptions and attitudes of workers. There are several culture frameworks currently in use across a variety of organizations and licensee contexts.
Licensees should ensure that the safety culture assessment framework is mapped against the five safety culture characteristics (see section 2 of this document), and is used at all stages of the assessment process.
3.3.2 Independent and self-assessments
There are different approaches to conducting a safety culture assessment. It may be conducted independently by an external organization or contractor, or as a self-assessment by workers within the organization. A safety culture assessment is generally a hybrid of these two types, using a blended team of independent contractors and workers who represent all areas of the organization.
Organizations that hire a contractor to conduct the assessment have the advantage of increased objectivity over the course of an assessment. However, consideration should be given to ensuring that the experience and insights gained from the assessment are retained within the organization. While self-assessments risk being less objective, they are more adaptable and offer learning and development opportunities for workers.
3.3.3 Assessment team selection
Selection of an appropriate assessment team is essential to ensuring the continual development and improvement of the assessment process and outputs.
The team should be selected to ensure adequate knowledge and expertise of safety culture and the organization’s technology. A best practice is to include representatives from another licensee organization or industry on the assessment team. Assessors involved in peer audits have more in-depth industry knowledge, and may also have an advantage relating to interviewees and interpreting data.
Team members should have knowledge and experience in:
- human factors and behavioural/social sciences
- qualitative and quantitative methods for cultural assessment
- assessments of safety culture
- various functional area specialties
- technologies of the organization
The overall team should reflect a balanced representation of the above, including consideration of worker demographics (age, gender, union representatives).
The assessment team lead(s) should be experienced and knowledgeable in safety culture, monitoring of safety culture, and assessment and improvement methods. The team lead’s responsibilities include:
- selecting team members and team member training, if necessary
- determining roles and responsibilities of team members
- planning and coordinating the assessment
- liaising with management and leadership (union, senior workers)
- communicating with the organization
- ensuring the organization is fully engaged in the assessment
- supervising the process of the assessment
- implementing measures to monitor and improve the assessment process where necessary
- producing preliminary and final reports
3.4 Safety culture assessment process
Figure 1: Safety culture assessment process
Safety culture assessment is an ongoing process and includes the following steps:
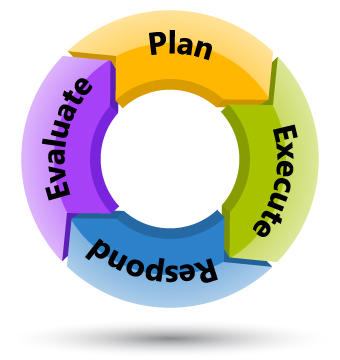
- Plan the assessment.
- Execute the assessment, analyze, and record results.
- Respond to the findings by developing and implementing an improvement plan.
- Evaluate the progress implementing the improvement plan while considering trends in safety culture in the period between assessments.
Although safety and security culture assessment methods are generally similar, a security culture assessment places additional emphasis on mitigating the risk (likelihood and consequences) of deliberate malicious acts. As a result, some expectations differ from a safety culture assessment, in areas such as information sharing and communications. [13]
3.4.1 Plan the assessment
A safety culture assessment involves systematically gathering, reviewing and analyzing culturally relevant data, and identifying and implementing improvement actions. This is to promote safety, learn about organizational factors affecting safety, and to continually seek an understanding of how culture operates within the organization.
Planning the assessment involves applying the chosen assessment method and associated framework, as well as finalizing details of how data will be collected, analyzed, interpreted and reported. Consideration and adoption of an assessment method should integrate a safety culture framework that includes key characteristics. A variety of safety culture frameworks are available. The licensee should be able to demonstrate that each characteristic in the CNSC’s safety culture reference framework is clearly and effectively addressed.
In determining the assessment method, several factors should be considered, including the organization’s size and complexity, and the risks and consequences associated with the licensed activity. At a minimum, the assessment should address the shared beliefs and attitudes on safety and security – at all levels and functional areas of the organization. Assessments of safety culture may include specific language and data-gathering tools tailored to specific topics and workers.
Understanding that safety culture can change over time will help an organization to maintain and improve safety. A maturity model should be used to describe and interpret the organization’s safety culture, so it can be monitored and improved (see appendix B).
3.4.2 Execute the assessment
During the assessment, the team lead(s) will make decisions about all aspects of the assessment plan (e.g., management interfaces/engagement, team member roles and training, effective application of a safety culture framework and method, reporting of results, and transition to actions).
Senior management should promote organization-wide participation in all aspects of the assessment via surveys, interviews and other assessment tools.
During the assessment, the team may need to refine its scope in order to identify possible patterns that warrant additional attention, data collection and analysis. Emergent themes identified throughout the assessment should lead to supplementary analysis and reflection. The assessment team should periodically review assessment objectives (such as those listed in section 3.1 of this document) to ensure adherence to methodological objectives.
3.4.3 Respond to the assessment and transition to action
Licensees should respond to assessment results by developing and implementing an improvement plan. This should include an analysis of the assessment results and offer opportunities for organizational leaders to reflect on these results. The report should outline the team’s findings, including supporting evidence aligned with the selected assessment framework. Any insights that the team can provide on the underlying cause of the findings will help develop the improvement plan. The process of translating assessment findings and insights into actions may be integrated into existing programs and processes, such as problem identification and resolution systems; corrective and preventive action programs; leadership reflection sessions; safety culture monitoring panels; and other organizational improvement processes.
The improvement plan represents a road map toward the organization’s vision of the desired safety culture, and it should contain goals and timelines for achieving them. The licensee should articulate or reaffirm this vision in subsequent communications; the characteristics of a healthy safety culture can help articulate and refine this vision, which should be compared to the current safety culture state based on the assessment. Any gaps will inform management as to where to focus the improvement plan, and identify positive characteristics that should be protected and fostered.
Licensees should prioritize improvements based on assessment results, with consideration to potential impact to safety and security, trends from previous assessments, and the unique context of their organization and work environment. How a licensee chooses improvements following an assessment, and the commitment to implementing these improvements, should be consistent with the existing management system and lead to improvements in established policies and procedures.
3.4.4 Evaluate progress and impact on safety culture
Licensees should periodically evaluate their progress by reviewing previous safety culture assessments and the resulting improvement plans, to determine how these actions have affected the organization’s safety culture.
The three-stage safety culture maturity model described in appendix B should be used as a tool to initially establish safety culture maturity and to monitor changes over time. The licensee’s assessment of its safety culture maturity should be included in the assessment report.
The licensee should continually monitor the health of its safety culture between safety culture assessments. Information from monitoring activities conducted should be analyzed and understood in the context of safety culture assessment results. If monitoring activities identify additional improvement opportunities, systematic consideration should be given to prioritizing and implementing these improvements.
Other safety culture monitoring activities may include:
- surveys, including topic-based surveys, worker surveys in focused areas, and follow-up surveys
- safety culture monitoring panels
- safety-related focus groups, town hall sessions or feedback tools
- opportunities for workers to discuss and reflect on their personal roles and responsibilities for safety
- seeking feedback on specific focus areas from workers, management, regulators, contractors or stakeholders
- trending and analysis of leading organizational performance indicators, previous safety culture assessments, and other organizational audits and evaluations
- trends in operational performance indicators detected through routine monitoring
- reflecting on formal and informal dialogue focused on safety between management and other workers
- potential for changes in safety culture following significant organizational changes, such as change in ownership, structure or responsibilities
- reporting of and responses to near misses, events or incidents
Licensees should consider these monitoring activities when planning subsequent assessments.
3.5 Record keeping
Records that should be retained for each safety culture assessment include those for the planning, implementation and analysis of safety culture assessments, as well as those for subsequent improvement plans and the implementation of improvement initiatives. This information will help the organization understand how its safety culture is evolving over time. The following are examples of records that should be retained:
- decisions, such as the rationale for the assessment’s scope and type
- assessment methods, timelines, and implementation
- lessons learned during each assessment cycle
- evaluations of progress against a safety culture maturity model (see appendix B)
- information related to organizational improvements, performance, or preventive actions
- impact analyses of improvement actions
4. Summary Report
Upon completion of a safety culture assessment, the licensee shall prepare a summary report for submission to CNSC staff. The licensee shall ensure the following information is described in the summary report:
- assessment goals
- assessment scope
- the chosen assessment method and associated safety culture framework
- overview of assessment results
- improvement plans
Guidance
The description of the safety culture assessment’s goals should explain how the assessment supports organizational objectives. An overview of how the safety culture assessment relates to relevant organizational programs and practices (e.g., corrective and preventive action programs, human performance programs, communications) should be included.
The description of the scope should provide a rationale for the organizational areas included in the assessment (e.g., departments, functions, workgroups, contractors).
A description of the assessment method and associated safety culture framework should include the following information:
- organizational context (size, risks, complexity of work) considered in determining the breadth and depth of data collection and analysis
- a discussion of how the data collection and analysis techniques applied are empirical, valid, practical, and functional
- an overview of each phase of the assessment including associated timelines
- informational or technical references to relevant safety culture frameworks, guidance, and best practices
An overview of results should provide a summary of the analysis process, including general themes as well as the organization’s strengths and opportunities for improvement. Assessment findings may concentrate on one specific area or topic, and should be based on organization-wide data. A description of the data and analysis should be included with each finding.
The description of improvement plans should discuss how the assessment findings are integrated with safety culture monitoring activities and the organization’s processes and practices to improve safety. Specific corrective/preventive actions should be described along with the expected results and timelines for implementation.
Appendix A: Applicable Requirements and Guidance, by Licence and Activity Type
Table A1 outlines which requirements and guidance in REGDOC-2.1.2, Safety Culture, apply to licensees, according to licence class and activity type.
| Class of license and activity type | Section of REGDOC-2.1.2* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section 2. Fostering Safety Culture | Section 3. Safety Culture Assessments | Section 4. Summary Report | ||
| Class I nuclear facility | Nuclear power plant | R | R | R |
| Other Class I nuclear facilities | R | G | G | |
| Uranium mine or mill | All | R | G | G |
| Class II nuclear facility | All | G | G | G |
| Nuclear substances and radiation devices | All | G | G | G |
| Transportation | All | G | G | G |
* R: requirement G: guidance / prudent management practice
Appendix B: Safety Culture Maturity Model
Understanding how safety culture changes over time, both positively and negatively, is essential to fostering safety culture. The safety culture maturity model presented here, as well as the associated indicators in Table B1, have been adapted from the following IAEA publications:
- IAEA-TECDOC No. 1329, Safety Culture in Nuclear Installations: Guidance for Use in the Enhancement of Safety Culture [15]
- INSAG-15, Key Practical Issues in Strengthening Safety Culture [10]
- Safety Series Report No.11, Developing Safety Culture in Nuclear Activities – Practical Suggestions to Assist Progress [11]
Note that specific activities or behaviours within an organization, group or team will often fit into more than one stage depending on the specific indicators used. Organizations, groups, or teams may fluctuate between these stages over time. Indicators are included under each of the three safety culture maturity stages below.
Safety culture and security culture have similar characteristics and share the same stages and indicators of maturity levels. The following safety culture maturity model can be also used to assess security culture maturity, so that it can be monitored and improved.
Stage 1: Requirement-driven
Safety is primarily reactive and driven by formal rules and management direction.
Safety is viewed principally as a technical and procedural issue related to worker safety. Adherence to established rules and externally imposed regulations become the overriding reasons for safety in the performance of work. Procedural violations are understood primarily as individual worker issues as opposed to as an outcome of organizational processes. Most workers believe that safety is primarily a responsibility of management or a designated authority, and that safety requirements and procedures are generally imposed upon them by others.
Stage 2: Goal-driven
Good safety performance becomes an organizational objective and is dealt with primarily in terms of safety goals.
There are processes and procedures for achieving safety goals. These processes are grounded in clear organizational objectives, which describe how specific organizational values and goals relate directly to safety. Improvement initiatives are administered and monitored by safety professionals, while workers have the option to contribute to improvements in safety performance. Safety targets are monitored for effectiveness and strengthened over time, and safety goals are systematically integrated across all areas. It is understood that worker performance depends on effective organizational systems.
Stage 3: Continually improving
Safety is seen as a continually improving and proactive process, beginning with all workers sharing a clear vision of and value for safety.
All workers, including managers and contractors are personally and actively involved in enhancing safety throughout the organization. Everyone has a clear understanding of safety-related requirements and how their own responsibilities contribute to achieving and sustaining enhancements to safety in their everyday tasks. Complacency towards risks and threats is identified and eliminated through attention to process safety, and all workers share a questioning attitude.
Table B1 describes specific behaviours related to the three stages of maturity of an organization’s safety culture.
| Indicator | Stage 1: Requirement-driven | Stage 2: Goal-driven | Stage 3: Continually improving |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | Problems are not anticipated, and the licensee reacts to each problem as it occurs. | The licensee concentrates primarily on day-to-day matters, with limited long-term focus on building value through safety | The licensee acts strategically with a focus on the longer term as well as awareness of the present. It seeks to anticipate problems and deal with their causes before they happen. |
| Communication and teamwork | Communication between individuals and departments is poor. Collaboration between departments and functional areas is not encouraged. | Management encourages cross-departmental and cross-functional teams and communication. Senior managers function as a team and coordinate departmental and functional decisions. | Workers recognize and demonstrate the need for collaboration between departments. They receive management support, recognition and resources needed to collaborate. |
| Response to errors | Most mistakes are hidden by work-arounds. Only mistakes with severe consequences are identified and are blamed on workers for their failure to comply with rules. | Management’s approach to mistakes is to put more controls in place via procedures and retraining; blaming workers is less prevalent. | Almost all mistakes are viewed in terms of work process variability. It is more important to the licensee to understand what has happened than to find someone to blame; this understanding is used to modify work processes and reinforce worker perceptions. |
| Role of management | Management is seen primarily as endorsing the rules, pushing workers, and expecting results. | Management’s role is seen as applying management techniques. | Coaching workers to improve safety performance is a part of management’s role. Management is accountable for modelling continual safety improvements. |
| Learning | There is little listening to or learning from safety-related experience inside or outside the organization. A defensive posture is assumed in the face of constructive criticism. | The licensee is somewhat open to learning from other organizations, especially techniques and best practices. | Learning from others both inside and outside the organization is valued; time is made available and devoted to adapting such knowledge to improve safety performance. |
| Value of safety ("safety-production balance") | Safety is viewed as a required nuisance. Short-term profit or productivity goals are seen as all-important and often take priority over safety. | Safety is thought to imply higher cost and reduced production. | Safety and production are seen as interdependent. |
| Stakeholder relationships | Regulators, suppliers, and contractors are treated cautiously or in an adversarial manner. | The licensee’s relationship with regulators, suppliers, and contractors are kept distant rather than close; there is a cautious approach where trust must be earned. | Collaborative relationships are developed between the licensee and regulators, suppliers, customers, and contractors |
| Value of diversity | Workers are viewed as "system components" who are defined and valued solely in terms of what they produce. Diversity is seen as a weakness. | Diversity is acknowledged as important, but rarely exploited. Diversity is used intermittently in decision-making. | Workers are respected and valued for their contribution to overall performance and for their knowledge of safety as applied. Diversity in opinions is sought and embraced. |
| Adherence to processes | There is little or no awareness of work or business processes. Expectations are not put in writing and are often assumed. | There is a growing awareness of the impact of influence of culture in the workplace. It is not understood why added controls do not yield the expected results in safety performance. Expectations are written and adherence is expected. | Workers believe in and follow work processes in the organization, and help managers to oversee them. |
| Conflict management | Dissenters are punished for their viewpoints. There is an adversarial relationship between management and other workers. | Dissenters are tolerated but not encouraged. Conflict is seen as disturbing, and is discouraged in the name of teamwork. | Questions are encouraged and dissenters’ viewpoints are appreciated. Conflict is recognized, and it is addressed by finding mutually beneficial solutions. Management and workers have a respectful and supportive relationship. |
| Systems view | Workers perform in isolation; "not my problem" is commonly heard. | Workers are cognizant of how their role and tasks performed affect the organization. | Workers are fully aware of broader organizational goals and how they contribute to them. Decisions are made in the full context of their safety impact on work or business processes, as well as on departments and overall safety performance. |
| Performance management | Performance incentives are not aligned with safety and security goals. Workers are rewarded for obedience and what they produce and deliver, regardless of long-term consequences. | Individual performance incentives are aligned with attaining safety and security goals. It is important to meet or exceed short term productivity goals; workers are rewarded for exceeding goals, regardless of the long-term results or consequences. | Performance incentives – both individual and collective – are aligned with attaining safety and security goals. Short-term performance is measured and analyzed so that changes can be made to improve long-term performance. The licensee rewards not only those who produce, but also those who support others’ work and the achievement of organizational goals, including safety. Workers are also rewarded for improving processes as well as results. |
| Feedback | Feedback is rarely given. | Feedback is given and improvement is consequently expected, regardless of context. | Feedback is routine and it becomes typical to use it to make improvements. |
| Training | Training is understood as an imposition and impediment to getting work done. | Training is understood as a necessity. | Training is understood as an investment. |
Glossary
- learning organization (organisation axée sur l’apprentissage)
- A work environment where people continually build on their capability to reach their goals, where new and challenging ways of interacting and behaving are encouraged in order to meet future organizational challenges, and where everyone has the opportunity to make sense of their work together.
- licensing basis (fondement d’autorisation)
A set of requirements and documents for a regulated facility or activity comprising:
- the regulatory requirements set out in the applicable laws and regulations
- the conditions and safety and control measures described in the facility’s or activity’s licence and the documents directly referenced in that licence
- the safety and control measures described in the licence application and the documents needed to support that licence application
- management system (système de gestion)
- The framework of processes, procedures and practices used to ensure that an organization can fulfill all tasks required to achieve its objectives safely and consistently.
Note: The management system integrates all elements of an organization into one cohesive system to enable all of the organization’s objectives to be achieved. These elements include the structure, resources and processes. Personnel, equipment and organizational culture, as well as the documented policies and processes, are parts of the management system. - safety culture assessment (évaluation de la culture de sûreté)
- A periodic evaluation of safety culture using a defined framework and method for data collection, analysis, interpretation and reporting.
- safety culture (culture de sûreté)
- The characteristics of the work environment, such as the values, rules, and common understandings that influence workers’ perceptions and attitudes about the importance that the organization places on safety.
- security culture (culture de sécurité)
- The assembly of characteristics, attitudes and behaviour of individuals, organizations and institutions that support and enhance nuclear security.
- worker (travailleur)
- A person who performs work referred to in a licence.
Note: Workers include contractors and subcontractors, as well as persons directly employed by a licensee.
References
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 7, Nuclear Security Culture, Vienna, 2008.
- CSA Group, N286-12, Management System Requirements for Nuclear Facilities, Mississauga, 2012.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. SF-1, Fundamental Safety Principles, Vienna, 2006.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GSR Part 1, Government, Legal and Regulatory Framework for Safety, Vienna, 2010.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-R-3, The Management System for Facilities and Activities, Vienna, 2006.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-G-3.1, Application of the Management System for Facilities and Activities, Vienna, 2006.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-G-3.5, The Management System for Nuclear Installations, Vienna, 2009.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. NS-G-2.4, The Operating Organization for Nuclear Power Plants, Vienna, 2001.
- IAEA, International Nuclear Safety Group report INSAG-24, The Interface Between Safety and Security at Nuclear Power Plants, Vienna, 2010.
- IAEA, International Nuclear Safety Group report INSAG-15, Key Practical Issues in Strengthening Safety Culture, Vienna, 2002.
- IAEA, IAEA Safety Series Report No.11, Developing Safety Culture in Nuclear Activities – Practical Suggestions to Assist Progress, Vienna, 1998.
- IAEA, IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 20, Objective and Essential Elements of a State’s Nuclear Security Regime, Vienna, 2013.
- IAEA, IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 13, Nuclear Security Recommendations on Physical Protection of Nuclear Material and Nuclear Facilities (INFCIRC/225/Revision 5), Vienna, 2011.
- IAEA, IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 14, Nuclear Security Recommendations on Radioactive Material and Associated Facilities, Vienna, 2011.
- IAEA, IAEA-TECDOC No. 1329, Safety Culture in Nuclear Installations: Guidance for Use in the Enhancement of Safety Culture, Vienna, 2002.
Additional Information
- Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, DIS-12-07, Safety Culture for Nuclear Licensees, Ottawa, 2012.
- CSA Group, N286.0.1-14, Commentary on N286-12, Management system requirements for nuclear facilities
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), IAEA-TECDOC No. 1707, Regulatory Oversight of Safety Culture in Nuclear Installations, Vienna, 2013.
- University of Georgia School of Public & International Affairs, 1540 Compass, Winter 2015 – Issue 8, "Examining the Interface between Nuclear Security Culture and Nuclear Safety Culture", Athens, Georgia, 2015.
- IAEA, (draft) technical guidance, Enhancing nuclear security in organisations associated with nuclear and/or radioactive material.
- Institute of Nuclear Power Operations, INPO 12-012, Traits of a Healthy Nuclear Safety Culture, Revision 1, Atlanta, 2013.
- Nuclear Energy Institute, NEI 09-07, Revision 1, Fostering a Healthy Nuclear Safety Culture, Washington, 2014.
- World Association of Nuclear Operators, PL 2013-1, Traits of a Healthy Nuclear Safety Culture, London, 2013.
CNSC Regulatory Document Series
Facilities and activities within the nuclear sector in Canada are regulated by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC). In addition to the Nuclear Safety and Control Act and associated regulations, there may also be requirements to comply with other regulatory instruments such as regulatory documents or standards.
Effective April 2013, the CNSC's catalogue of existing and planned regulatory documents has been organized under three key categories and twenty-five series, as set out below. Regulatory documents produced by the CNSC fall under one of the following series:
- 1.0 Regulated facilities and activities
- Series 1.1 Reactor facilities
- 1.2 Class IB facilities
- 1.3 Uranium mines and mills
- 1.4 Class II facilities
- 1.5 Certification of prescribed equipment
- 1.6 Nuclear substances and radiation devices
- 2.0 Safety and control areas
- Series 2.1 Management system
- 2.2 Human performance management
- 2.3 Operating performance
- 2.4 Safety analysis
- 2.5 Physical design
- 2.6 Fitness for service
- 2.7 Radiation protection
- 2.8 Conventional health and safety
- 2.9 Environmental protection
- 2.10 Emergency management and fire protection
- 2.11 Waste management
- 2.12 Security
- 2.13 Safeguards and non-proliferation
- 2.14 Packaging and transport
- 3.0 Other regulatory areas
- Series 3.1 Reporting requirements
- 3.2 Public and Aboriginal engagement
- 3.3 Financial guarantees
- 3.4 Commission proceedings
- 3.5 CNSC processes and practices
Note: The regulatory document series may be adjusted periodically by the CNSC. Each regulatory document series listed above may contain multiple regulatory documents. For the latest list of regulatory documents, visit the CNSC's website.