REGDOC-2.12.2, Site Access Security Clearance
Preface
This regulatory document is part of the CNSC's Security series of regulatory documents, which also covers high-security facilities and security for nuclear substances. The full list of regulatory document series is included in the back of this document and can be found on the CNSC's Web site at nuclearsafety.gc.ca/regulatorydocuments.
Regulatory document REGDOC-2.12.2, Security: Site Access Security Clearance sets out the guidance of the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) for granting, denying or revoking a site access security clearance (SASC) for authorized unescorted entry to a protected area at a high-security site.
Requirements associated with this document are found in the Nuclear Safety and Control Act (NSCA) and regulations made under it.
This document is intended to form part of the licensing basis for a regulated facility or activity. It is intended for inclusion in licences as either part of the conditions and safety and control measures in a licence, or as part of the safety and control measures to be described in a licence application and the documents needed to support that application.
Important note: Where referenced in a licence either directly or indirectly (such as through
licensee-referenced documents), this document is part of the licensing basis for a regulated facility or
activity.
The licensing basis sets the boundary conditions for acceptable performance at a regulated facility or activity
and establishes the basis for the CNSC's compliance program for that regulated facility or activity.
Where this document is part of the licensing basis, the word "shall" is used to express a requirement, to
be satisfied by the licensee or licence applicant. "Should" is used to express guidance or that which is
advised. "May" is used to express an option or that which is advised or permissible within the limits of
this regulatory document. "Can" is used to express possibility or capability.
Nothing contained in this document is to be construed as relieving any licensee from any other pertinent
requirements. It is the licensee's responsibility to identify and comply with all applicable regulations and
licence conditions.
Table of Contents
- 1.0 Purpose
- 2.0 Scope
- 3.0 Relevant Legislation
- 4.0 Process for Granting, Denying or Revoking a Site Access Security Clearance
- 5.0 Application Process for a Site Access Security Clearance
- 6.0 Reporting to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission
- 7.0 Site Access Security Clearance Renewal Process
- 8.0 Transferability
- 9.0 Record Retention
- 10.0 Termination of Employment
- 11.0 Appeal Process
- Appendix A
- Appendix B
- Appendix C
- Appendix D
- Glossary
- References
1.0 Purpose
This document provides guidance regarding the process for granting, denying, renewing or revoking a site access security clearance (SASC) for authorized unescorted entry to a protected area. The purpose of a SASC is to prevent unreasonable risk to high-security sites. This includes risks to operations, personnel, safety and national security from the insider threat.
2.0 Scope
This document sets out a comprehensive approach and process for granting, denying or revoking a SASC.
3.0 Relevant Legislation
The provisions of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act (NSCA), General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations (GNSCR) and Nuclear Security Regulations (NSR)relevant to this document include:
Paragraph 9(a) of the NSCA, which provides that "the objects of the Commission are (a) to regulate the development, production and use of nuclear energy and the production, possession and use of nuclear substances, prescribed equipment and prescribed information in order to
- prevent unreasonable risk, to the environment and to the health and safety of persons, associated with that development, production, possession or use,
- prevent unreasonable risk to national security associated with that development, production, possession or use, and
- achieve conformity with measures of control and international obligations to which Canada has agreed"
Subsection 24(4) of the NSCA, which provides that "No licence may be issued, renewed, amended or replaced
unless, in the opinion of the Commission, the applicant (a) is qualified to carry on the activity that the licence
will authorize the licensee to carry on; and (b) will, in carrying on that activity, make adequate provision for the
protection of the environment, the health and safety of persons and the maintenance of national security and
measures required to implement international obligations to which Canada has agreed."
Subsection 24(5) of the NSCA, which provides that "A licence may contain any term or condition that the
Commission considers necessary for the purposes of this Act."
Subsection 12(1)(c) of the GNSCR, which provides that "Every licensee shall take all reasonable precautions to
protect the environment and the health and safety of persons and to maintain the security of nuclear facilities and
of nuclear substances."
Section 17(1) of the NSR, which provides that "No person shall enter a protected area without physical proof of
the recorded authorization of the licensee."
Subsection 17(1.1) of the NSR, which provides that "In this section, 'site access security clearance' means a
clearance granted by a licensee to a person based on a security assessment for site access security clearances
referred to in the Personnel Security Standard or on an equivalent security assessment."
Subsection 17(1.2) of the NSR, which provides that "A site access security clearance is valid for five
years."
Subsection 17(2) of the NSR, which provides that "Subject to section (3), a licensee shall, before issuing an
authorization to enter a protected area to a person, prepare an identification report that contains the following
information and documents:
- the person's name and date and place of birth;
- documentary proof of the person's lawful presence in Canada;
- the address of the person's principal residence;
- a photograph depicting a frontal view of the person's face;
- the person's occupation; and
- a copy of the site access security clearance for that person."
Subsection 17(5) of the NSR, which provides that "An authorization to enter a protected area may be issued for
any term not exceeding five years and shall be subject to any terms and conditions that are necessary to minimize
the risk to the security of the area."
Subsection 17(6) of the NSR, which provides that "Every licensee shall give to a person who has sought an
authorization to enter a protected area, on the person's request, a copy of any information or documents referred to
in subsection (2) that the licensee possesses."
Subsection 18.4 of the NSR, which provides that "An authorization may be issued for any term not exceeding five
years and shall minimize the risk to the security of the facility."
Section 21 of the NSR, which provides that "A licensee may revoke an authorization."
Subsection 37. (1) of the NSR, which provides that "Every licensee shall:
- keep a record of the name of each person to whom an authorization has been issued;
- retain the record for one year after it expires or is revoked."
4.0 Process for Granting, Denying or Revoking a Site Access Security Clearance
4.1 Site access security clearance assessment
Licensees should have processes in place, as part of their SASC measures, to assess the levels of risk presented by applicants and renewals. Furthermore, the SASC measures should clearly set out established threshold criteria to trigger these processes.
The SASC assessment process consists of two parts:
- an assessment of reliability, which is normally conducted by the licensee
- a security assessment of loyalty and reliability as it relates thereto, which is conducted by the Canadian Security Intelligence Service (CSIS) with input from the licensee
When assessing reliability, a licensee should verify a person's character, honesty, background, qualifications and trustworthiness. The purpose of the SASC assessment is to determine if a person may access prescribed information or assets without posing an unreasonable risk to the protected area, to the personnel working there or to national security. Individuals who have been granted a security clearance equivalent to a Level II, Secret Clearance, may be required to have access to designated and/or classified information on a need-to-know basis. The CSIS security assessment may include a subject interview conducted by CSIS to collect further information in order to make a determination on loyalty and/or reliability as it relates to loyalty.
The SASC process is comparable to the Government of Canada (GOC) security screening process. For more information and a comparison of the processes, see table 1 in appendix D.
The licensee's SASC measures will be assessed as part of the CNSC compliance program, in order to determine if it is satisfactory or not.
4.2 Application process
The process for application should include the following:
- the licensee obtaining written consent from the applicant to conduct the necessary investigations (licensee & CSIS)
- the applicant providing the necessary information to apply for the appropriate level of clearance (SASC or Level II equivalent)
- the licensee conducting a briefing to the applicant on his/her responsibilities and certifying the clearance.
4.3 Collection and verification of information
Before granting a SASC, the licensee should carry out the following activities:
process the SASC application in order to determine an applicant's five-year traceable history, by collecting and assessing the following information:
- personal data, including history of residence, for the five years immediately preceding the SASC application or, if the applicant is under 21 years of age, to age 16
- criminal records name check (CRNC) in accordance with Canadian Police Information Centre policy
- educational/professional qualifications
- employment history
- CSIS security assessment
perform the requisite checks identified in the
Policy on Government Security (PGS) - Personnel Security Standard Appendix C, or an equivalent policy or
standard
verify all required information, either personally or via a trusted third party
endorse the reliability of the applicant upon requesting a security assessment from CSIS
process and verify the completeness of information for a security assessment before sending it to CSIS; verification
of necessary information for reliability assessments takes place in parallel with the loyalty assessment that CSIS
carries out in support of a SASC application or renewal.
4.4 Missing or adverse information
In cases of gaps in documentation (boxes not checked, initials missing), the licensee should inform the applicant about it and ensure the information is complete. If there are gaps in history (residence or employment), the licensee should contact the applicant to retrieve all necessary information and, if deemed necessary, meet with the applicant to clarify any concerns.
In a case of an indictable conviction, the licensee should conduct a security interview with the applicant. The criteria used to decide whether a security interview is necessary should include assessing the risk to site and national security. Failure by the applicant to declare all criminal convictions will delay the SASC process and may result in the denial of reliability screening.
4.5 Licensee decision
The decision to grant, deny or revoke a SASC rests with the licensee. The decision should be supported by a licensee policy that includes a risk-based decision-making process and should also take into consideration any potential or unreasonable risks to national security.
5.0 Application Process for a Site Access Security Clearance
5.1 Consent and authorization
The SASC application should begin with the licensee obtaining the appropriate authorization to conduct personnel screening of an applicant. The applicant must give the licensee written authorization to conduct such screening. This authorization can be granted by using the Treasury Board Secretariat (TBS) Personnel Screening Consent and Authorization Form (TBS/SCT 330-23E: Rev. 2006/02), where all data is collected in sections A to C and signed off in sections D and E. See appendix A for the Web links to the TBS form, and appendix B for the application process map.
Before permitting the applicant to start completing the Personnel Screening Consent and Authorization Form, the licensee should advise the applicant that failure to include all required information, or to complete the form in an accurate or legible manner, will result in documentation being returned, thereby delaying the screening process. The licensee should also explain to the applicant the consequences of attempting to conceal any information that could affect the degree of confidence that the licensee could place in him or her.
The licensee completes section A of the form and the applicant completes sections B and C. For section C, the applicant must initial the required boxes and sign the bottom of this section. The licensee must complete the appropriate boxes. The licensee then completes sections D and E to confirm review and approval.
A credit check may be required, depending on the applicant's position, access to financial information and funds, or signing authority. A credit check may also be conducted for cause, which includes personal bankruptcy or a related criminal conviction record, such as fraud.
5.2 Screening process
Once the licensee has obtained consent to screen the applicant, and the screening process has been approved, the applicant should provide all pertinent information to apply for a SASC. This can be done by using the TBS Security Clearance Form (TBS/SCT 330-60E), where all compulsory data is collected as determined by the licensee. See appendix A for a list of web links to the TBS forms, and appendix B for the application process map.
In addition, the applicant should provide notarized/certified translations for all supporting documentation (e.g., educational certificate, CRNC, professional qualifications) that is not in English or French.
5.2.1 Personal data
The licensee should verify the applicant's full name, date and place of birth. The place of birth should include the city or town name, province (state) and country.
Verified original documentation should include two pieces of validly issued government identification from the following list:
- birth certificate
- passport
- valid work permit
- permanent resident card
- Canadian citizenship card or other government-issued photo identification
At least one piece of photo identification should contain a current facial view of the applicant.
5.2.2 Less than five years of traceable history in Canada
The licensee should have a verification process for SASC applicants who have less than five years of traceable history within Canada.
An applicant who has resided or worked in a country outside of Canada for a period of more than six months within the last five years should provide a CRNC for each country of previous residence where the individual was 16 years of age or older. An applicant who resided in a country where only local checks (e.g., immediate area where the applicant resided) are completed should have a CRNC (or equivalent) completed for each area where the person resided. The applicant should also have a CRNC completed by the country's state government policing authorities.
Where there are no reciprocal arrangements between different policing authorities, the applicant should obtain a CRNC from each authority. For example, for an applicant residing in the United States, a CRNC and fingerprint check should be conducted at the county, state and federal levels by the Federal Bureau of Investigation's National Crime Information Center.
Where CRNC information is unavailable or incomplete, or an indictable conviction exists, fingerprints should be verified through a police service agency (in the area of jurisdiction where the person has resided) or by a trusted third party. There are several countries that do not have a CRNC process in place. In such cases, the onus is on the licensee to verify criminal conviction information from a trusted third party.
5.2.3 Foreign nationals
A foreign national should provide identification (e.g., work visa or passport) and proof of legal status in Canada to the licensee. A foreign national should also provide, via a trusted third party, a CRNC from the person's country of origin. A CRNC should be provided for each country where a foreign national has resided for a period of six months or more during the past five years, including all areas and all police authorities within the country where the person resided.
A SASC should be granted to the individual according to the licensee's security protocols, risk management processes and the licensee's SASC measures. Enquiries can only be conducted in countries that have bilateral/reciprocal agreements with Canadian investigative authorities.
5.2.4 Employment and education records
The licensee, or a trusted third party on behalf of the licensee, should verify the applicant's education and/or professional qualifications (e.g., licence, degree or diploma) and record them by way of a certified copy. The licensee should initial and date the copy and retain it on file for audit purposes. The licensee may use an internal form or record that is signed or certified by the licensee representative to indicate that all records verified are valid.
5.2.5 Criminal activity assessment
Where a CRNC check conducted by the licensee, or a trusted third party on behalf of the licensee, is incomplete, fingerprints should be taken for verification and a security interview should be performed to collect more information.
When an applicant has an indictable conviction, the licensee should review the criminal history and assess the risk to personnel safety and/or security to the nuclear facility based on this information. The risk assessment should include an assessment of criminal convictions and any information provided by police agencies that may affect the reliability of a SASC applicant or renewal, such as links to organized crime. It should also consider the nuclear facility's operations, including what facility areas or nuclear material to which the individual may have access. A criminal conviction, including a self-declaration by the applicant, that identifies adverse information, will also require a security interview or an alternate process that suitably assesses risk.
The licensee should have, as part of its SASC measures, a process to assess risk for personnel with a criminal conviction record who are being transferred to an assignment or position that requires access to sensitive information, assets or vital areas. The transfer of an individual within a high-security site should trigger a process to assess risk.
5.2.6 CSIS notice of assessment
CSIS will provide the licensee with a notice of assessment (NOA), indicating that adverse information exists from the security assessment or that there is no adverse information (NOA - NO ADV INFO) concerning the applicant who requires a SASC. The SASC is valid for five years from the date of notification from CSIS, with the provision that CSIS may review the SASC for cause at any time.
There are three types of notices from CSIS: 1) NRT - NO REPORtable trACES; 2) NRT - INSUFFICIENT INFO; and 3) NOA - BRIEF. For the first two notices, the licensee may continue the application process, following a risk-based decision making process. For the third notice, the licensee must hold the file and await more detailed information from CSIS investigators, who will send a formal letter to the licensee and a copy to the CNSC.
5.3 Security interview
5.3.1 Adverse information
If an application results in the discovery of adverse information, a security interview may be required. If the declaration of a criminal conviction contains circumstances related to adverse information, the licensee should conduct a security interview to adequately assess any potential risk to the site (protected area), including its operation and personnel, and to identify any threat that may have national security implications.
5.3.2 Threat and risk assessment
One of the purposes of a security interview is for the licensee to assess risk. An interview should be conducted based on adverse information, as well as for cause. For example, if an applicant had been convicted of fraud, and the licensee discovered that the person had provided false information in regard to professional qualifications, a security interview should be conducted to assess risk. Security interviews with the potential for elevated risk should be conducted by two interviewers. (See appendix C to read the risk-based decision-making process.)
A SASC may be reviewed at any time for cause. The licensee's SASC measures should have established threshold criteria that will "trigger" a security interview or an alternate process that suitably assesses risk. This could include the circumstances of the criminal offence (nature, frequency, passage of time, indictable vs. summary, etc.). Licensees must also consider potential risk to the site or national security, given the duties and tasks to be assigned to the individual being considered for the granting of a SASC.
To determine if the applicant poses a potential threat or risk to the site, the licensee should conduct a security interview or have measures in place to suitably address the following situations:
- the resolution of incomplete or questionable documentation
- poor or questionable credit history
- indictable convictions
- past criminal activity
- less than five consecutive years of traceable history
- adverse or insufficient information from CSIS
- any other adverse information that has potential risk to site or national security
5.3.3 Documentation
The applicant should bring all required documentation to the security interview. This material should include original or verified copies of all documentation related to the SASC, including:
- proof of legal status (citizenship, marital, etc.)
- notarized or certified translation (if not in English or French) of all CRNCs
- passport or visa
- educational certificates, diplomas or degrees
The licensee's security interview may require a detailed analytical examination of information provided by the applicant, or lack thereof, to verify reliability/authenticity where other means of verification are not available. The security interview may also include other verification tools, in order to establish the applicant's reliability.
5.3.4 Interviewer qualifications
A licensee's security interview should be conducted by an experienced interviewer with the requisite training and skills, who may be a member of the licensee's SASC process. The licensee determines the qualifications of the interviewer.
Licensees should utilize interviewers trained in forensic interviewing techniques to conduct interviews related to the assessment of a SASC applicant or renewal, or for cause. A forensic interviewing techniques course should include essential subjects such as detecting deception, conducting a structured interview and analyzing statements. For further guidance on suitable courses, licensees may contact the CNSC's Nuclear Security Division.
5.3.5 Record-keeping
The licensee should have documented processes in place for conducting security interviews and evaluating interview results. The documentation and the associated information should be suitably protected and kept on file.
5.3.6 Decision to grant, deny, renew or revoke
The licensee should identify a senior program authority who decides to grant, deny, renew or revoke a SASC based on the results of the licensee's risk-based decision-making process, including reliability/loyalty checks and, if conducted, the security interview.
5.4 Granting of a site access security clearance
The licensee may grant a SASC with or without certain limitations and restrictions to access prescribed information or assets.
5.4.1 Determinative assessment - security interview
If a security interview is deemed necessary and determines the applicant does not pose a security risk, the licensee may grant a SASC without restrictions as long as the CSIS assessment has not identified any adverse information. The licensee may impose security restrictions with cause (e.g., limitations on hours of work or access to certain areas of the licensed facility and nuclear material) while a SASC is in the process of being updated over an extended period of time. Restrictions should be imposed only if the licensee has not identified adverse information that could indicate an unreasonable risk to the health and safety of persons, or to site and national security.
5.4.2 Restrictions to control access
Restrictions may be imposed based on the licensee's own governance for risk tolerance / acceptance. The licensee should take into consideration the sensitivity and vulnerability of certain critical areas, vital areas and inner areas. When granting a SASC, the licensee has the authority, under subsection 17(5) of the Nuclear Security Regulations, to implement any terms and conditions necessary to minimize the risk to the security of the protected area.
An applicant may, based on a risk assessment, obtain limited unescorted site access that is subject to certain restrictions (e.g., limited hours of work; a standalone computer not connected to the facility network and with no Internet connection; or no access to prescribed information, prescribed equipment, nuclear material or nuclear material accounting, or to classified information or assets). Restrictions should be recorded, clearly communicated, and subject to a documented review process conducted by the licensee.
5.4.3 Alternative work
If the licensee becomes aware that a SASC holder has been charged with a serious criminal offence or the licensee is made aware of significant adverse information, the SASC holder should be assigned alternative work duties until the charge is adjudicated in court or the information is assessed by the licensee. The applicant should be placed under appropriate administrative controls and access control measures, as well as be monitored through the Supervisory Awareness Program at the licensed site.
5.4.4 Denial of a site access security clearance
An applicant should not be granted a SASC if, after the security interview or other checks, a risk assessment determines that:
- SASC requirements are not met
- an unreasonable risk is posed to the site, including its operation and personnel
- a threat or an unacceptable risk is posed that may have a negative impact on site and national security
No applicant should be granted a SASC if the person refuses to be interviewed or if the licensee or CSIS identifies adverse information that is considered a security threat or risk to the facility.
5.5 Revocation of a site access security clearance
No person should retain his or her SASC - or be processed for a SASC - if he or she refuses to be interviewed, or if the licensee identifies adverse information that is considered a security threat or risk to the facility. If a current SASC holder refuses to be interviewed, the SASC should be revoked.
5.6 Certification
Once the decision has been made to grant a SASC, the licensee should provide a comprehensive briefing (preferably in person but may be done remotely) to the applicant explaining the individual's future security responsibilities and obtain acknowledgement from the person in writing. This can be done by using the TBS Security Screening Certificate and Briefing Form (TBS/SCT 330-47), where all data is collected in sections A and B, acknowledgement is declared in section C, and sign-off is completed in section D. See appendix A for a list of Web links to the TBS forms, and appendix B for the application process map.
A SASC constitutes the authority for a licensee to allow access to prescribed information or assets. A SASC alone does not confer a right of access to classified information assets or sites and does not give a successful SASC applicant (SASC holder) access to classified information or assets, including those from a third party. The applicant must seek a security clearance (Level I and above) for access to classified information or assets. Individuals who have been granted a security clearance equivalent to a Level II Secret Clearance may have access to designated and/or classified information on a need-to-know basis. Access to designated/classified information may only be granted by the author of the designate/classified document.
The TBS Policy on Government Security governs the Personnel Screening Standard to ensure that only persons whose reliability, trustworthiness and loyalty to Canada have been established are granted access to classified information, assets or sites. It is important to note that no individual is entitled, by virtue of rank or position, to have access to, knowledge of, or custody of classified information and assets. The individual must have the appropriate Personnel Security Clearance level and an identified "need to know". (Access includes the opportunity to gain knowledge of information by visual or auditory means.) Private-sector organizations do not have the authority to grant any level of GOC security clearance without CNSC sponsorship, which provides for the necessary arrangements with CSIS and the RCMP (See table 1 in appendix D).
6.0 Reporting to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission
6.1 Site access security clearance granted
SASCs should be granted to applicants who have met all the requirements of the application process. However, the licensee may decide to grant a SASC with or without restrictions despite the following circumstances:
- the applicant has not met the basic SASC requirements, and the licensee is unable to resolve gaps subsequent to a security interview
- CSIS provides the licensee with a notice of assessment indicating there is insufficient information (NRT-INSUF)
- CSIS or a police agency identifies adverse information that may indicate a security risk.
In such cases, the licensee should inform the CNSC and provide justification for its decision.
If a SASC holder's circumstances change and these may pose a risk to operations, personnel, safety and national security, the licensee should investigate. Where necessary, the SASC holder should forward a complete report of the change of circumstances through the holder's manager to the licensee, who should forward it on to the CNSC as required. The licensee may deny this individual access to prescribed information and assets, until the situation is resolved.
Measures taken by the licensee to mitigate security concerns and risk acceptance, as identified by circumstances defined in sections 5.2.5 and 5.4.1 of this document, may be subject to CNSC review, to ensure they are in accordance with paragraph 9(a) (ii) of the NSCAand paragraph 12(1) (c) of the GNSCR.
6.2 Site access security clearance denied or revoked
Where a SASC is denied or revoked, the licensee should inform the CNSC and provide detailed information on why the SASC was denied or revoked, along with the following:
- the level of threat or risk that the individual poses to site or national security
- the source of the information that was used in making the decision (e.g., law enforcement or security agencies)
- the results of any related or ongoing investigation
- the CSIS security assessment brief
6.3 Communication protocols
The licensee should report to the CNSC as per requirements. Licensees have regulatory obligations for notifying the CNSC in writing, concerning several areas related to the security of a nuclear facility.
7.0 Site Access Security Clearance Renewal Process
The licensee should have an auditable SASC renewal process, which should include checks that ensure enough time is available to complete and consider all required verifications and other assessments before the SASC expires. This will ensure that all relevant assessment information is reviewed and assessed before a SASC is renewed, and that any adverse information that is discovered will be available and on record where a SASC is not renewed for valid reasons.
8.0 Transferability
A valid SASC may be transferable from one high-security site to another, provided there is a CNSC-approved SASC process in place at both sites. To the extent permitted by law, any adverse information and restrictions on the applicant should be shared between licensees during the transfer of a SASC. It is the licensee's prerogative to decide whether to accept the transfer of a valid SASC holder to its licensed site.
The SASC of an individual may be transferred between licensees, provided the following criteria have been met:
- the SASC is valid, with no adverse information
- the SASC is not due for updating before the transfer can take place
- as necessary, the individual has self-declared in writing that there have been no changes in his/her personal history regarding criminal convictions
9.0 Record Retention
The licensee should maintain a current listing of all persons who have been granted or denied a SASC or who were subject to the revocation of their SASCs for tracking, updating and auditing purposes. Because of their sensitivity, verified copies of all SASC documentation (dated and signed) containing personal information should be retained in an organization's security file and safeguarded appropriately. Verified copies of all SASC documentation should be subject to the licensee's governance regarding the protection, retention and destruction of documents. Designated/classified documents should be protected according to TBS guidelines on the protection of these documents. Documents related to security interviews or risk assessments should be made available on a need-to-know basis to the appropriate CNSC staff upon request.
10.0 Termination of Employment
Licensees should establish a procedure for dealing with the termination of employment of individuals who possessed a SASC or the equivalent of a Level II Secret Clearance and are no longer employed onsite. The procedure should include a formal debriefing (preferably in person, but may be done remotely), to remind individuals of their continuing responsibilities relating to the protection of prescribed (or designated/classified) information to which they had access in the course of their employment. If the termination is a result of a SASC review, the licensee must abide by section 6.2 of this guide.
11.0 Appeal Process
The licensee should have an appeal process whereby an applicant who was denied or revoked a SASC can request a review of the application in order to clarify items of concern or provide new information. An appeal process should include the capacity to:
- organize and utilize a body of individuals that would oversee and conduct the process
- implement and respect consistent timelines for the conduct of the process
- allow for the request and verification of information by the licensee and submission of additional information by the applicant
- make information available to the applicant that describes the appeal process, including how submitted information is reviewed
- have a process for decision making regarding the appeal process, including how the applicant is advised of the appeal process decision and any subsequent actions and implications for the applicant or former SASC holder
Appendix A
The following forms, as amended from time to time, may be used for a SASC application, and can be downloaded from the TBS Web site:
- Personnel Screening, Consent and Authorization Form (TBS/SCT 330-23E)
- Security Clearance Form (TBS/SCT 330-60E)
- Security Screening Certificate and Briefing Form (TBS/SCT 330-47)
Licensees may use their own forms for the SASC application process in order to distinguish their internal SASC form from the Government of Canada forms listed above, provided the SASC forms meet all applicable regulations.
Appendix B
Site Access Security Clearance - Application Process
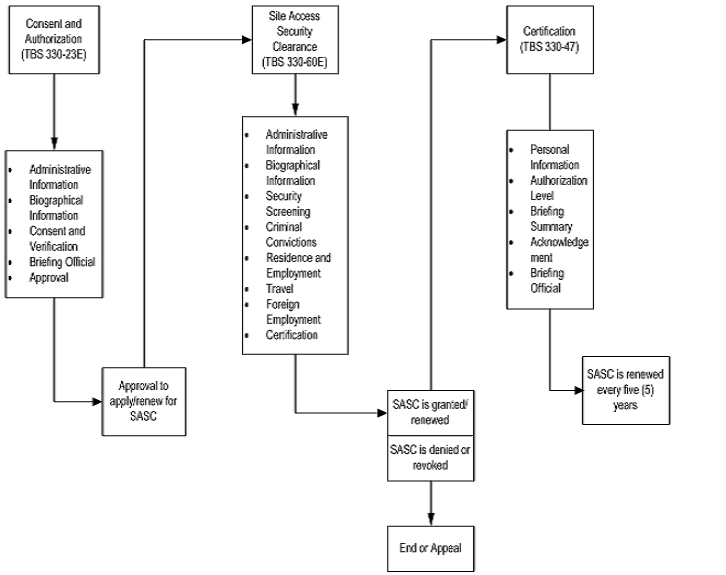
Application Process text version
Appendix C
Site Access Security Clearance Risk-Based Decision-Making Process
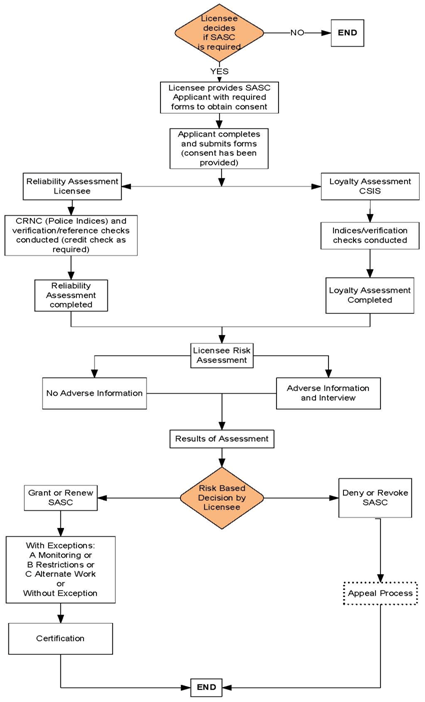
Risk-Based Decision-Making Process text version
Appendix D
|
Nuclear Safety and Control Act, Nuclear Security Regulations and General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations |
Treasury Board Secretariat |
|
|---|---|---|
Sensitivity level |
||
Prescribed |
Classified |
|
Compromise would affect the security of the high-security site, its operations or its personnel. |
Compromise would affect an interest other than the national interest or the national security of Canada. |
Compromise would affect the national interest or the national security of Canada. |
Required markings |
||
|
Prescribed Information |
Protected "A" |
Level I, Confidential |
|
Protected "B" |
Level II, Secret |
|
|
Protected "C" |
Level III, Top Secret |
|
Security classification |
||
|---|---|---|
SASC only |
SASC + security clearance |
SASC + security clearance |
|
Employees, contractors, visitors:
|
Employees, nuclear security officers (NSOs), physical protection support staff, intelligence analysts: SASC + "need to know"
|
Employees, nuclear security officers, security systems technicians, intelligence analysts: SASC + "need to know"
Note: including a two-person rule |
Glossary
- adverse information
-
Information about a SASC applicant or holder - whether collected by the licensee, outside agencies or a trusted
agent - that is questionable in nature, unclear, or does not match the information provided by the applicant.
The information collected may indicate:
- a gap in history
- a poor credit rating
- a criminal conviction
- links to a criminal element
- concerns related to the reliability or trustworthiness of a SASC applicant or holder
- applicant
- Any person applying for a SASC to a high-security site in Canada. Note: CNSC staff who are not inspectors and/or do not hold a Level II Secret GOC clearance will apply for a CNSC SASC to work at the licensed facility.
- criminal records name check (CRNC)
- A search used to determine if a person has a criminal record. The search can be based on name and date of birth or - for much greater assurance - on fingerprints, for positive identification.
- for cause
-
- A threshold for action (interview, further checks, denial, revocation, suspension).
- In the context of a security assessment, a determination that more in-depth verifications are required due to gaps in information or information that could not be verified.
- A determination by the licensee that sufficient evidence exists regarding an unreasonable security risk to the licensed site, including its operation and personnel, or a threat with national security implications.
- foreign national
- A person who is not a Canadian citizen or a permanent resident of Canada.
- high-security site
- A nuclear power plant or a nuclear facility where Category I or II nuclear material (as defined in the Nuclear Security Regulations) is processed, used or stored.
- indictable conviction
- A category of conviction under the Canadian Criminal Code reserved for more serious offences such as murder, acts of terrorism, robbery, drug trafficking, treason and certain types of sexual assaults.
- insider threat
- An individual with authorized access to a nuclear facility or transport, who might attempt unauthorized removal or sabotage, or who could aid outsiders to do so.
- interviewer
- A qualified person, representing the licensee, who conducts investigations and/or security interviews in order to gather information from a SASC applicant or holder, for the purpose of granting, renewing, denying or revoking a SASC.
- licensing basis
-
A set of requirements and documents for a regulated facility or activity comprising:
- the regulatory requirements set out in the applicable laws and regulations
- the conditions and safety and control measures described in the facility's or activity's licence and the documents directly referenced in that licence
- the safety and control measures described in the licence application and the documents needed to support that licence application
- Notice of assessment (NOA) - INSUFFICIENT INFO
- A Canadian Security Intelligence Service (CSIS) notice of assessment indicating that there is insufficient information for CSIS to provide a meaningful assessment on the applicant's loyalty to Canada, usually due to lack of traceable history or residency.
- NOA - NO ADVERSE INFO
- A CSIS notice of assessment indicating that there is no adverse information regarding an applicant's loyalty to Canada.
- protected area
- An area surrounded by a barrier that meets the requirements of section 9 of the Nuclear Security Regulations.
- security interview
- An interview conducted by a qualified investigator representing the licensee, where information is collected to confirm or deny adverse information.
- trusted third party
-
- For CRNC: A private organization or agency that is in partnership with the Canadian Police Information Centre (or equivalent) for the purposes of conducting name-based criminal record verifications.
- For references: A private organization or agency contracted by the licensee for the purposes of conducting reference verifications.
References
- Policy on Government Security, 2009. Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
- IAEA Nuclear Security Series No. 8, Implementing Guide, Preventive and Protective Measures against Insider Threats, Vienna, 2008.
- The International Training Course (ITC 22 - 2010), Physical Protection of Nuclear Facilities and Materials, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA.
- Industrial Security Manual, 2012. The Public Works Government Services Canada - Industrial Security Program.
CNSC Regulatory Document Series
Facilities and activities within the nuclear sector in Canada are regulated by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC). In addition to the Nuclear Safety and Control Act and associated regulations, there may also be requirements to comply with other regulatory instruments such as regulatory documents or standards.
Effective April 2013, the CNSC's catalogue of existing and planned regulatory documents has been organized under three key categories and twenty-five series, as set out below. Regulatory documents produced by the CNSC fall under one of the following series:
- 1.0 Regulated facilities and activities
- Series
- 1.1 Reactor facilities
- 1.2 Class IB facilities
- 1.3 Uranium mines and mills
- 1.4 Class II facilities
- 1.5 Certification of prescribed equipment
- 1.6 Nuclear substances and radiation devices
- 2.0 Safety and control areas
- Series
- 2.1 Management system
- 2.2 Human performance management
- 2.3 Operating performance
- 2.4 Safety analysis
- 2.5 Physical design
- 2.6 Fitness for service
- 2.7 Radiation protection
- 2.8 Conventional health and safety
- 2.9 Environmental protection
- 2.10 Emergency management and fire protection
- 2.11 Waste management
- 2.12 Security
- 2.13 Safeguards and non-proliferation
- 2.14 Packaging and transport
- 3.0 Other regulatory areas
- Series
- 3.1 Reporting requirements
- 3.2 Public and aboriginal engagement
- 3.3 Financial guarantees
- 3.4 Commission proceedings
- 3.5 Information dissemination
Note: The regulatory document series may be adjusted periodically by the CNSC. Each regulatory document series listed above may contain multiple regulatory documents. For the latest list of regulatory documents, visit the CNSC's Web site at nuclearsafety.gc.ca/regulatorydocuments.
Page details
- Date modified: